Unveiling the Truth About Quantum Computing
Unveiling the Truth About Quantum Computing
Imagine a world where computers can process information at speeds unimaginable today, solving complex problems in minutes that would take classical computers thousands of years. This is the promise of quantum computing, a revolutionary field at the intersection of physics, mathematics, and computer science.
The Basics of Quantum Computing
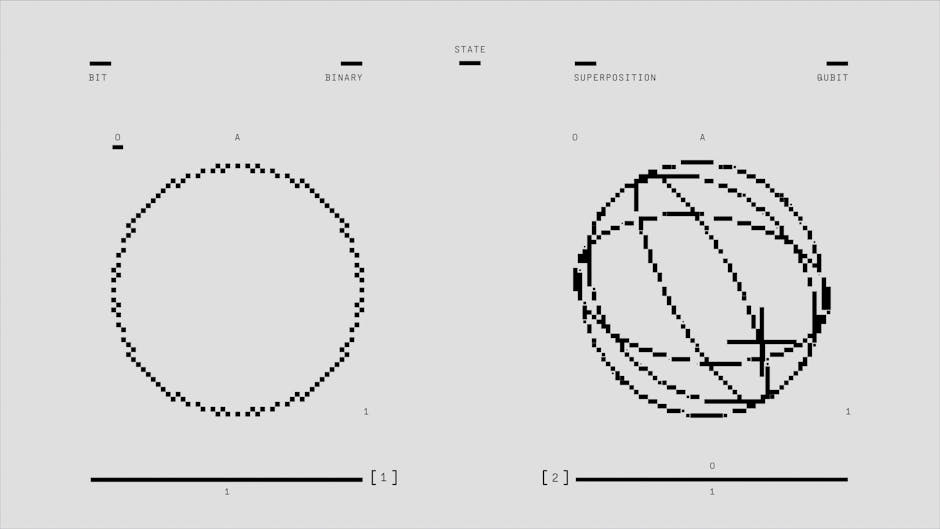
At the heart of quantum computing are quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously thanks to the principles of superposition and entanglement. While classical bits can only be 0 or 1, qubits can be 0, 1, or both at the same time, leading to exponential processing power.
Key Concepts:
- Superposition: Qubits can be in multiple states at once.
- Entanglement: Qubits can be correlated in a way that the state of one qubit depends on the state of another, regardless of the distance between them.
- Quantum Gates: Operations that manipulate qubits to perform calculations.
Applications of Quantum Computing
While still in its infancy, quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize various fields, including:
- Encryption: Quantum computers could break current encryption algorithms, leading to the need for quantum-resistant cryptography.
- Drug Discovery: Quantum algorithms could accelerate the process of drug discovery by simulating molecular interactions.
- Optimization: Quantum computers excel at solving optimization problems, from logistics to financial modeling.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promise, quantum computing faces several challenges, such as:
- Noisy Qubits: Quantum systems are prone to errors due to environmental interference.
- Scalability: Building large-scale quantum computers remains a significant engineering feat.
- Decoherence: Qubits lose their quantum properties over time, limiting computation.
Quantum Computing vs. Classical Computing
| Aspect | Classical Computing | Quantum Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Power | Sequential processing | Parallel processing |
| Information Representation | Binary (0s and 1s) | Superposition of states |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How does superposition enable quantum computing?
A: Superposition allows qubits to exist in multiple states simultaneously, exponentially increasing processing power.
Q: What is quantum entanglement?
A: Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where the state of one qubit is dependent on the state of another, even at a distance.
Q: Are quantum computers a threat to cybersecurity?
A: While quantum computers could break current encryption, research is ongoing to develop quantum-resistant cryptography.
Q: When will we see practical quantum computers in everyday use?
A: While progress is rapid, widespread adoption of quantum computers may still be years away due to technical challenges.
For more information on the latest developments in quantum computing, stay tuned to our [Related Article].
In Conclusion
Quantum computing holds the promise of revolutionizing how we process information, solve complex problems, and drive innovation across industries. While challenges remain, the potential for quantum supremacy is within reach. As we continue to unlock the secrets of the quantum realm, the future of computing holds endless possibilities.
Are you ready to dive into the world of quantum computing and explore its limitless potential? Join us on this exciting journey towards a quantum future.